For over a decade, FxScouts Nigeria has been reviewing forex brokers and providing in-depth analyses. Our extensive research and unique testing methodology ensures that all broker reviews are accurate and fair, with hundreds of thousands of data points generated annually. Since 2012, we’ve tested over 180 brokers across global and African markets. Our team of professionals are frequently cited in global and regional media, shaping market conversations and trends.
-
Best Forex Brokers
Our top-rated Forex brokers
-
NGN Trading Accounts
Save on conversion fees
-
Brokers for Beginners
Start trading here
-
Forex Demo Accounts
Learn to trade with no risk
-
ECN Brokers
Trade with Direct Market Access
-
No-Deposit Bonuses
Live trading with no deposit
-
High Leverage Brokers
Extend your buying power
-
Lowest Spreads Brokers
Tight spreads and low commissions
-
Islamic Account Brokers
Best accounts for Muslim traders
-
Market Maker Brokers
Fixed spreads & instant execution
-
MetaTrader 4 Brokers
The top MT4 brokers in Nigeria
-
MetaTrader 5 Brokers
The top MT5 brokers in Nigeria
-
TradingView Brokers
The top TradingView brokers
-
cTrader Brokers
The top cTrader brokers in Nigeria
-
Forex Trading Apps
Trade on the go from your phone
-
Copy Trading Brokers
Copy professional traders
-
All Trading Platforms
Find a platform that works for you
75-90% of retail traders lose money trading Forex and CFDs. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs and leveraged trading work and if you can afford the high risk of losing your money. We may receive compensation when you click on links to products we review. Please read our advertising disclosure. By using this website you agree to our Terms of Service.
- XM - Low Spreads, Fast Trade Execution, and Excellent Education
- FP Markets - Best VIX Trading Broker
- AvaTrade - Trade VIX on MT4 and MT5
- HFM - VIX Trading on a Micro Account
- Pepperstone - VIX Trading with 100:1 Leverage
- XTB - Low-Cost VIX Trading
- IC Markets - VIX Futures Trading
- IG - Trade VIX and 19,200 Other Instruments
What is the Volatility 75 Index (VIX)?
The VIX is the most watched volatility index in the global markets. It measures expected volatility in the S&P 500 but is also a barometer for confidence in the wider US stock market. The VIX is calculated by tracking the underlying price of S&P 500 options, not the stock market itself, allowing it to estimate the 30-day volatility of the S&P 500.
When the VIX reading is above 30, it implies high expected volatility and investor fear about the market’s direction. By contrast, a reading below 30 suggests investors are generally confident about the market outlook. In March 2020, amid concern about the impact of the outbreak of the COVID-19 pandemic on the global economy, the VIX jumped to 82.69, its highest level ever, as stock markets crashed around the world.
During highly volatile periods, investors tend to dump stocks and buy “haven” assets considered more stable in times of uncertainty, such as US Treasury bonds or gold. High VIX readings are usually associated with poor stock market performance, which means it can be a useful tool for traders looking to hedge or short the market. The VIX can also be traded as a CFD, though not all brokers will offer it.
How did we choose the best brokers for trading the VIX?
The VIX is part of the indices asset class of financial instruments offered by online CFD brokers. We have an experienced review team dedicated to evaluating CFD brokers, so you don’t have to. Our team of experts meticulously examines each broker in 7 different areas using over 200 individual metrics. We invest hundreds of hours annually researching and scrutinising brokers to ensure we only recommend the best.
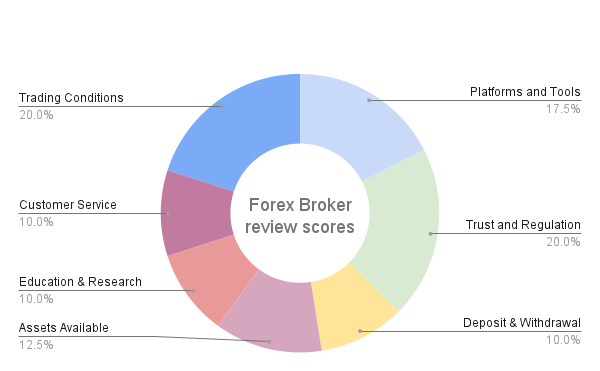
Of these seven areas, we always prioritise regulation and costs. These are our priorities because traders want to know that their broker is trustworthy and isn’t overcharging them. Brokers are constantly altering the products they offer, and we keep our reviews updated with the latest data. You can find out more about our in-depth review process here.
XM – Low Spreads, Fast Trade Execution, and Excellent Education
XM, a highly-regulated market maker, offers a comprehensive range of financial instruments, including Forex, stocks, commodities, equities, precious metals, energies, shares, a notable portfolio of 58 cryptocurrencies, and the sought-after VIX, Volatility Index Futures (S&P500) as a futures CFD. Its VIX offering is particularly enticing, with industry-leading spreads narrowing to just 0.05. Upholding a commitment to trading excellence, XM enforces a strict no-requotes and no-rejections policy, ensuring an impressive 99.53% of all trades are executed within a second on both MT4 and MT5 platforms.
Additionally, XM offers an expansive educational suite for traders at all levels. This includes daily Q&A sessions, live education weekdays from 05:00 to 15:00 GMT, meticulous platform tutorials, educational videos, and Forex webinars presented by 67 renowned experts across 19 languages. The inclusion of exclusive Forex seminars and top-notch market analysis resources ensures traders are well-equipped to navigate the trading landscape confidently.
FP Markets – Best VIX Trading Broker
FP Markets offers low-cost trading services, fast trade execution, and an excellent range of third-party trading platforms and trading tools, making it popular for traders worldwide. FP Markets’ accounts have a 100 AUD (or equivalent) minimum deposit and spreads of 1 pip (EUR/USD) on its commission-free Standard Account. Its Raw Spread Account offers spreads of 0 pips (EUR/USD) in exchange for a commission of 6 USD.
FP Markets offers VIX trading through the purchase of exchange-traded funds (ETFs) and exchange-traded notes (ETNs) that are linked to the Index. With an average spread of 0.16 on the VIX Index CFD FP Markets’ costs are about average, and leverage is up to 100:1, which is also similar to other brokers.
AvaTrade – Trade VIX on MT4 and MT5
One of our favourite brokers in Nigeria, AvaTrade is for traders who want a trusted broker with low costs, free withdrawals, and a well-designed mobile trading app. While AvaTrade’s minimum deposit of 100 USD isn’t the lowest you can find, it’s still low enough for most beginners. Avatrade offers some of the best trading tools in the industry alongside a world-class selection of educational and market analysis materials.
AvaTrade offers the VIX as a Short-Term Futures ETN, with a typical spread of 1.5 – about average compared to other brokers on this list. Available on both MT4 and MT5, Avatrade’s VIX ETN features a maximum leverage of 20:1 – lower than other brokers on this list – and it’s only available for USD accounts. As an ETN (similar to ETFs, but rather than holding a basket of stocks, ETNs are debt instruments with a maturity date), trading on the VIX at AvaTrade is only available Monday – Friday from 08:00 – 17:00 EST.
HFM – VIX Trading on a Micro Account
HFM is a fantastic all-around broker, with fast and free deposits and withdrawals and low cost trading accounts. HFM supports the MT4 and MT5 platforms in addition to its own new HFM trading app. It also has excellent trading tools to assist traders, such as free Autochartist.
Like most of the other brokers on this list, HFM offers VIX trading as an index CFD. The typical spread on the VIX at HFM is 0.14 – about average compared to other brokers – and maximum leverage is 100:1. We really like HFM’s Micro Account for beginners with its 5 USD minimum deposit, and the VIX is available here too. The only limitation to trading the VIX on the Micro Account is that the maximum contract size is 7 lots, compared to 60 lots on the Premium and Zero accounts.
Pepperstone – VIX Trading with 100:1 Leverage
Pepperstone’s low-cost ECN trading service, fast trade execution, and range of third-party trading platforms has made it popular amongst experienced traders and serious beginners around the world. One of our favourite Forex brokers, Pepperstone also excels when it comes to commodity and index trading.
We like Pepperstone’s simple pricing structure for trading the VIX, with 1 lot equating to a $1 per point move in the index. With an average spread of 0.16 on the VIX Index, CFD Pepperstone’s costs are about average, though minimum spreads may be much lower. A high leverage of 100:1 is available, though this is lower than the 200:1 for most other indices at Pepperstone but still more than enough for most traders.
XTB – Low-Cost VIX Trading
A well-regulated broker, XTB will appeal to traders looking for a wide choice of tradable instruments, low trading fees, top-class educational materials, and excellent market analysis. XTB’s xStation 5 trading platform offers many of the trading features found in MetaTrader 4, including one-click trading, multiple order types, price alerts, and real-time performance statistics, but also includes built-in market analysis and education. We find it is particularly easy for beginners to pick up and learn, and it’s available in your browser and as a mobile app for iOS and Android.
VIX trading at XTB is can be very low cost in comparison to other brokers, with a minimum spread of 0.11. However when we checked the spreads for this review, the spread was at 0.15, and XTB targeted a spread of 0.20. VIX trading leverage at XTB is 67:1, lower than other brokers on this list. But the main draw remains the xStation 5 platform, with its intuitive design and range of tools and features.
IC Markets – VIX Futures Trading
An excellent all-around broker, IC Markets was founded in 2007 in Australia and holds licences from some of the strictest regulators in the world. IC Markets is well-known for its low trading costs, choice of trading platforms, and wide range of trading tools. It also has some of the best education available from any broker.
Instead of an index, IC Markets offers the VIX as a Futures CFD. All IC Markets Futures CFDs are priced directly from the underlying futures markets, with commissions, financing charges and dividend adjustments all built into the spread itself. Be aware that IC Markets Futures CFDs are set to expire two working days before the contract expires on the underlying market. Futures CFDs are complex CFDs, so make sure you understand how they function before attempting to trade them.
IG – Trade VIX and 19,200 Other Instruments
| 🏦 Min. Deposit | USD 0 |
| 🛡️ Regulated By | ASIC, BaFin, DFSA, CFTC |
| 💵 Trading Cost | USD 6 |
| ⚖️ Max. Leverage | 200:1 |
| 💹 Copy Trading | No |
| 🖥️ Platforms | MT4, L2 Dealer, ProRealTime |
| 💱 Instruments | Bonds, Commodities, Cryptocurrencies, Digital 100s, Stock CFDs, ETFs, Forex, Indices, Interest Rates |
IG is one of the world’s largest CFD brokers, with 320,000 clients and over 19,200 CFDs to trade. IG has two low-cost trading accounts with no minimum deposit requirements and low costs. Instruments available to trade include commodities, indices, cryptocurrencies, over 16,000 shares and ETFs, options, interest rates and bonds. All CFDs can be accessed on IG’s award-winning app and web trader platform.
With such a large CFD line-up, it’s unsurprising that IG offers the VIX as a tradeable index CFD. Leverage is much lower than other brokers, at 5:1, and the spread rarely varies from 0.2 – relatively high compared to other brokers on this list. Note that IG prices the VIX index differently from the rest of its index markets. IG creates a price between the two nearest futures contracts on the underlying market, as these tend to be the most liquid markets.
Why trade the VIX?
Unlike indices, such as the S&P 500 or FTSE, which are groups of company shares, the VIX is a volatility index. The VIX tends to rise with increased market instability. Conversely, if the VIX falls, it signifies stable markets and an increase in the S&P 500.
Traders often use the VIX to hedge their portfolios against market downturns. For example, if you go long on shares in a US company but want to offset potential losses if the market takes a downturn, you would buy the VIX. Taking a long position on the VIX could potentially balance out drawdowns you may experience and hedge your market exposure. Because the VIX exhibits a negative correlation with other asset classes, it can reduce your overall risk and increase returns.
Some traders also speculate on the direction of the VIX itself rather than using it as a hedge. Depending on their outlook for market volatility, they may take long or short positions in VIX futures or options CFDs.
How Volatility trading works
Before you trade the VIX, you need to understand how volatility trading differs from standard CFD trading. Volatility is a measure of the movement of an asset’s price (in this case, the expected movement of the S&P 500 index over the next 30 days) rather than a measure of the price itself. So with volatility trading, rather than focusing on the direction of change, you are speculating on how much the market will move and how frequently that movement will occur.
As mentioned, the VIX and S&P 500 are strongly negatively correlated. That means that when the VIX increases, the S&P 500 is likely falling, and when the VIX falls, the S&P 500 is likely rising.
Going long or going short on the VIX
When you open a position on the VIX, you can either take a long or a short position. If you take a long position, you believe that volatility will increase; if you take a short position, you believe it will decrease. Although there is a strong negative correlation between the VIX and the S&P 500, volatility traders are not interested in whether the price of the S&P 500 will rise or fall, as they can profit from both price movements.
Going long on the VIX
Traders often choose a long position on the VIX during times of financial instability, when there is a lot of uncertainty and fear in the market. For example, if you had taken a long (buy) position on the VIX at the beginning of the Covid pandemic when it hit 82.7 per cent volatility, you would have made a substantial profit.
Going short on the VIX
Traders take short positions during times of low volatility and generally when they expect the S&P500 to rise in value. Low interest rates and economic growth usually result in the steady growth of the S&P500’s share prices, so traders short-sell the VIX, expecting that volatility will remain low during these conditions. However, it can be risky to short-sell the VIX, as losses can be significant if volatility spikes.
The benefits and risks of trading VIX CFDs
Benefits of Trading VIX CFDs
Trading the VIX allows traders to generate profits from the expected volatility of the S&P 500 index. It also has many other benefits:
- Easy Access and Flexibility: Traders can open an account with a broker and trade on a VIX CFD with a relatively small amount of capital. They can open or close positions anytime during the trading day and choose their trade size.
- Go long or short: You can speculate on VIX price movements in both directions. Traders generally buy (go long on) the index when uncertainty rises in the markets since uncertainty will likely result in heightened fear and greater volatility. Equally, when investors feel confident, volatility will likely decrease, so traders that sell (or go short on) the index may profit.
- Leverage: VIX CFD brokers allow traders to use leverage, which means they can trade with a smaller initial investment than they would need to trade VIX futures or options directly. This can magnify potential returns but also magnify potential losses, so it’s important to use leverage judiciously and manage risk carefully.
- Lower costs: Trading VIX CFDs can be cheaper than trading VIX futures or options, as there are lower transaction fees and no need to pay for margin financing. However, traders should be aware that other costs may be associated with CFD trading, such as overnight swap fees.
- Diverse trading strategies: VIX CFDs can be used in various trading strategies, such as speculating on volatility spikes, hedging against market downturns, or taking advantage of market inefficiencies.
Disadvantages and risks of trading the VIX 75 via CFDs
While there are significant benefits to using CFDs to trade the VIX 75, there are also considerable risks that any trader should be aware of before trading these complex financial products.
- Leverage: When you trade with leverage, you are essentially borrowing money from your broker to increase the size of your position. While this can potentially increase your profits, it also increases your risk of loss. If the market moves against you, your losses can be significantly magnified.
- Constant monitoring: You must always be alert to possible changes in your position. News announcements and other economic events can increase volatility significantly. This may cause rapid price changes that cause the balance of your account to change quickly. This is especially true if you have taken a short position on the VIX.
- It is easy to take on too much risk: Because the cost of trading the VIX is low due to leverage, it is easy for traders to be lulled into a false sense of security and take on higher trading positions than is prudent.
- Limited liquidity: VIX CFDs are less liquid than other financial instruments, such as major currency pairs or stock indices. This can lead to wider bid-ask spreads, slippage, and difficulty executing trades at the desired prices.
The role of CFD brokers in trading the Volatility 75 index
Brokers play a role in facilitating trading on the VIX. They act as intermediaries between traders and the exchange, executing trades on behalf of their clients. The broker provides traders with the platforms, tools, and resources needed to analyse market trends, place trades, and manage their trading accounts.
Brokers also offer traders leverage to benefit from larger trading positions with only a small amount of capital. The broker may provide other services, such as educational resources and customer support.
Important considerations when choosing a broker for trading the Volatility 75 index
When choosing a broker to trade the VIX, there are several important considerations to keep in mind:
- Regulation: You must ensure that the broker is legitimate and trustworthy. Reputable brokers are regulated by financial authorities such as the Financial Sector Conduct Authority (FSCA) in South Africa, the Financial Conduct Authority (FCA) of the UK, the Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC), and the Cyprus Securities and Exchange Commission (CySEC). Check whether your broker has a regulatory licence, and then check with the regulator that the licence is valid.
- Trading Platforms: Traders should choose brokers that offer a variety of stable and user-friendly trading platforms. Trading platforms should provide useful features such as technical indicators, risk management tools, and various charting tools. Third-party platforms, such as MetaTrader 4, MetaTrader 5, and cTrader, are popular among traders because they are available at most brokers, and traders can customise and save their settings should they migrate to another broker.
- Trading Fees: Trading fees include spreads, commissions, and overnight swap fees. Brokers must publish their trading fees on their websites, and traders should choose brokers with competitive spreads and commissions, as these fees can significantly impact profitability.
- Leverage: The broker should offer flexible leverage options for trading the Volatility 75 index. Leverage can magnify profits and increase risks, so traders should choose a leverage level that matches their risk appetite and trading strategy.
- Customer Support: The broker should provide excellent customer support through various channels, including live chat, email, and telephone. Traders should be able to contact the broker at any time and receive prompt and helpful assistance.
- Education and Research: The broker should provide educational resources and research materials to help traders improve their skills and stay informed about market developments. This can include webinars, tutorials, market analysis, and trading signals.
- Deposit and Withdrawals: The broker should offer convenient and secure deposit and withdrawal options, including bank transfers, credit/debit cards, and e-wallets. Traders should also check the broker’s withdrawal policy and processing times.
Using the VIX 75 as a Risk Management Tool
The VIX can also be used as a risk management tool. Because the VIX provides information on levels of implied volatility, it can help determine trade sizes. During periods of higher volatility (high VIX levels), it is prudent to reduce your lot sizes, whereas, during periods of lower volatility (lower VIX levels), you can increase your lot sizes.
Forex Risk Disclaimer
Trading Forex and CFDs is not suitable for all investors as it carries a high degree of risk to your capital: 75-90% of retail investors lose money trading these products. Forex and CFD transactions involve high risk due to the following factors: Leverage, market volatility, slippage arising from a lack of liquidity, inadequate trading knowledge or experience, and a lack of regulatory protection. Traders should not deposit any money that is not considered disposable income. Regardless of how much research you have done or how confident you are in your trade, there is always a substantial risk of loss. (Learn more about these risks from the UK’s regulator, the FCA, or the Australian regulator, ASIC).
Our Rating & Review Methodology
Our State of the Market Report and Directory of CFD Brokers to Avoid are the result of extensive research on over 180 Forex brokers. These resources help traders find the best Forex brokers – and steer them away from the worst ones. These resources have been compiled using over 200 data points on each broker and over 3000 hours of research. Our team conducts all research independently: Testing brokers, gathering information from broker representatives and sifting through legal documents. Learn more about how we rank brokers.
Editorial Team

Chris Cammack
Head of Content
Chris joined the company in 2019 after ten years experience in research, editorial and design for political and financial publications. His background has given him a deep knowledge of international financial markets and the geopolitics that affects them. Chris has a keen eye for editing and a voracious appetite for financial and political current affairs. He ensures that our content across all sites meets the standards of quality and transparency that our readers expect.

Alison Heyerdahl
Senior Financial Writer
Alison joined the team as a writer in 2021. She has a medical degree with a focus on physiotherapy and a bachelor’s in psychology. However, her interest in forex trading and her love for writing led her to switch careers, and she now has over eight years experience in research and content development. She has tested and reviewed 100+ brokers and has a great understanding of the Forex trading world.

Ida Hermansen
Financial Writer
Ida joined our team as a financial writer in 2023. She has a degree in Digital Marketing and a background in content writing and SEO. In addition to her marketing and writing skills, Ida also has an interest in cryptocurrencies and blockchain networks. Her interest in crypto trading led to a wider fascination with Forex technical analysis and price movement. She continues to develop her skills and knowledge in Forex trading and keeps a close eye on which Forex brokers offer the best trading environments for new traders.































































